What Is Uvulitis And Why Can It Occur?
Uvulitis is an inflammation of the uvula, a small fusiform muscle hanging from the lower edge of the soft palate, above the root of the tongue. This structure is better known by the general population as a bell or gullet.
Uvulitis is usually caused by infectious processes, allergic reactions, injuries after medical procedures, or consumption of inappropriate substances. If you want to know everything about this clinical picture, read on.
What is uvulitis?
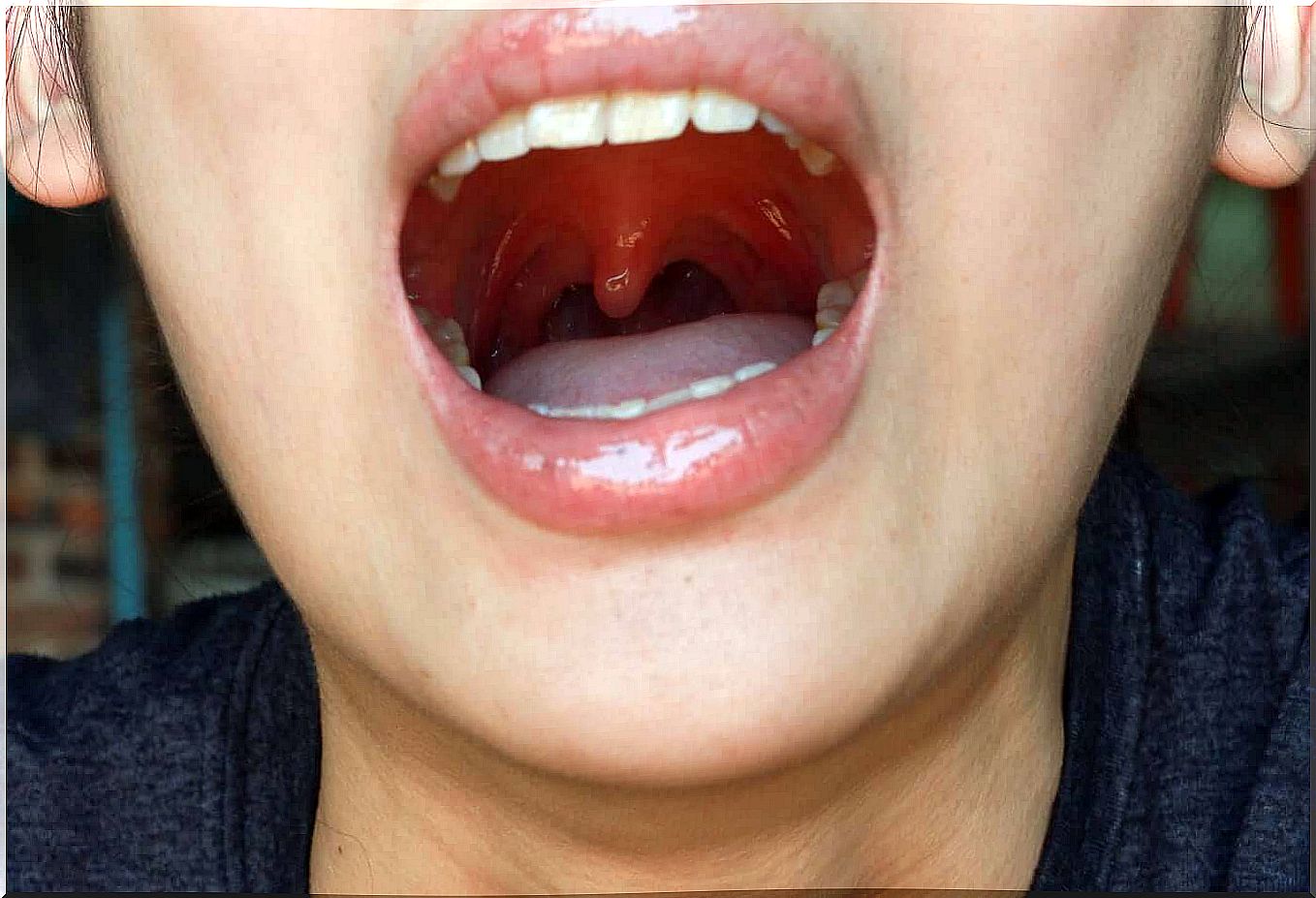
According to the US National Cancer Institute (NIH), the uvula is a piece of soft tissue that hangs in the back of the mouth. While this structure was previously believed to be merely vestigial, it was found to have a clear purpose: it helps prevent food from entering the nasal cavity.
The Medigraphic medical portal defines uvulitis as “a cellulitis – a tissue infection – which courses with erythema (redness), edema (accumulation of fluid), pain, fever and irritating cough”. It should be noted that, although bacterial or viral infection is the most common trigger of this pathology, it is by no means the only one.
What are its causes?
According to the US National Library of Medicine, the most common cause of uvulitis is an infection with streptococci, a group of bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Up to 30% of acute pharyngitis is associated with Streptococcus pyogenes, a disease largely related to uvulitis.
Other pathogenic infectious agents that cause this clinical picture are H. Influenzae type B and Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). In addition, infectious uvulitis occurs more often in young patients during school time and presents a clear seasonal pattern, especially in temperate regions. The peak of susceptibility occurs at 5, 10 and 12 years of age.
Infectious uvulitis is not the only possible variant of this disease. The non-infectious type, in turn, can be caused by the events listed below:
- An injury to the back of the throat.
- An allergic reaction to pollen, dust, dead skin cells from pets, or certain foods.
- Inhaling or swallowing certain toxic elements by mistake.
- Surgery, such as having tonsils removed, and other medical procedures, such as having an endoscopy.
- Smoke.
uvulitis symptoms
The patient should suspect uvulitis caused by an acute infection when the uvula is more inflamed compared to the pharynx and if there is also evidence of a low-grade fever. Among the most common general symptoms, we find the following:
- Fever if it arises as a result of an infection.
- Sensation of something stuck in the throat, accompanied by choking or choking.
- Cough.
- Pain on swallowing.
- Excessive saliva production.
- Little appetite.
According to the Colgate professional portal, if the symptoms of uvulitis do not disappear after a few days or white spots appear at the back of the mouth, it is possible that the patient is suffering from streptococcal pharyngitis. It occurs much more often in children, but adults can have it too.
Diagnosis and treatment
The Drugs.com medical portal shows that there are several diagnostic tests available to detect the underlying reasons for a patient’s uvulitis. Among them, we find the following:
- Blood tests: may be needed to assess the patient’s general health and rule out certain events.
- Throat culture: a sample of the oral mucosa is obtained and cultured in a specialized medium. This is used to detect the possible germs causing uvulitis if it is infectious.
- Allergy testing: the inflammation of the uvula may arise as a result of an allergic process. Allergen detection is essential to avoid this clinical picture and others that are much more serious, such as anaphylactic shock .
- Neck X-ray: mainly done on patients who have difficulty swallowing.
As far as treatment is concerned, it will vary according to the cause. In the case of bacterial uvulitis, specific antibiotics to combat the pathogen will be prescribed, while in the case of allergic origin, antihistamines will be needed. Steroids also reduce inflammation.
home care
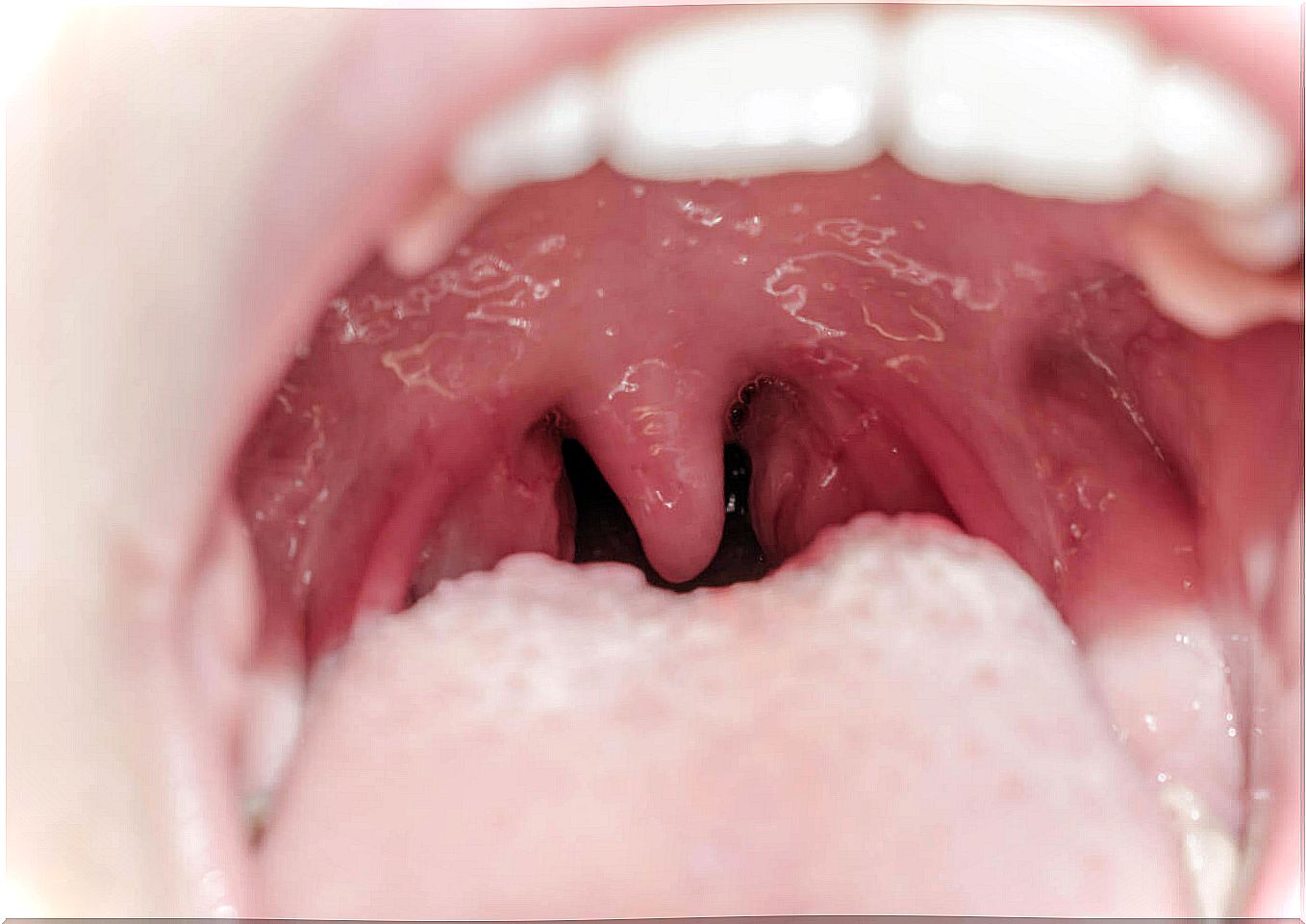
According to the UFhealth portal, there are several steps a patient can take at home to improve symptoms. Among them, we want to highlight the following:
- Rest. Uvulitis can resolve on its own or with treatment in 1-2 days.
- Drink plenty of fluids and gargle with warm salt water to reduce inflammation.
- Use sprays that help reduce itchy throat.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers. This reduces the pain caused by inflammation of the uvula.
- Do not smoke and avoid inhaling smoke, as both events cause irritation in the throat.
Follow your doctor’s instructions.
As you read along these lines, uvulitis is a sign of another underlying condition, not a disease itself. From infections to allergic conditions, the reasons that cause an inflammation of the uvula can be very varied.
This condition usually resolves with proper treatment within 1-2 days. The method of intervention will depend entirely on the causative agent, since a bacteria is not fought in the same way as an allergic inflammation.